Biomass is one of the oldest sources of energy. However, significant ambiguity and misunderstanding surround the question of whether biomass is a renewable or non-renewable energy source. Can biomass truly be considered a renewable option for meeting our energy needs? Does it qualify as an efficient source of energy? Let’s explore this through the following article!
What is Biomass?
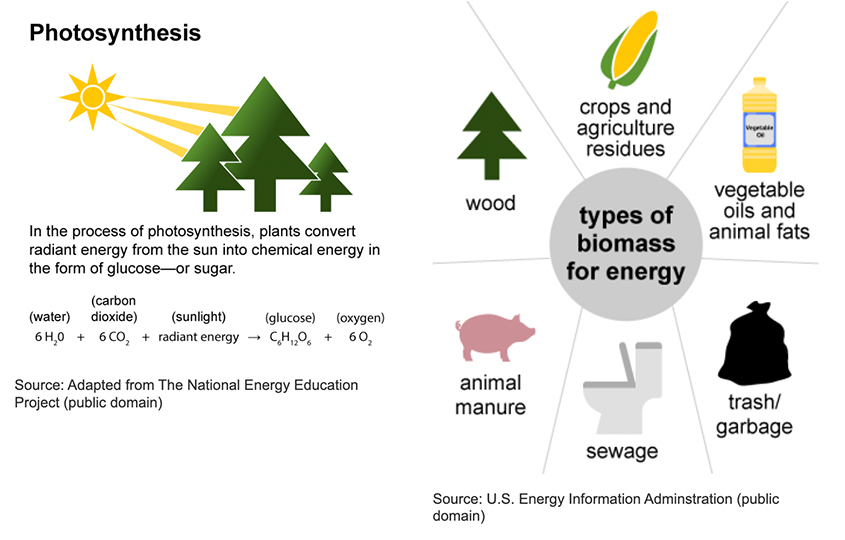
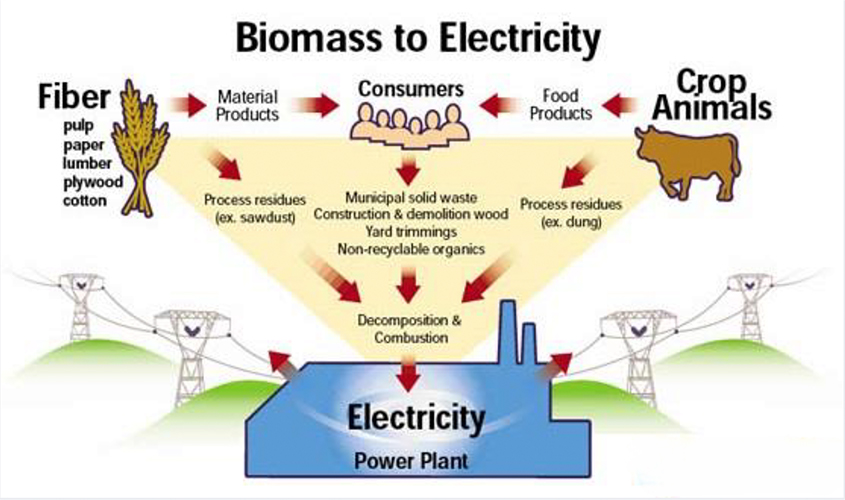
Biomass refers to organic matter derived from plants and animals that can be utilised as a fuel source. When combusted, biomass can generate heat for warming water, residential heating, and various other applications. In many developing nations, biomass remains a crucial energy resource. It is available in diverse forms, including:
- Wood and agricultural residues (such as crop waste, forestry byproducts).
- Organic components of municipal solid waste.
- Animal and human waste streams (manure, sewage sludge).
- Other industrial process wastes like sawmill residues and black liquor.
Biomass is considered an alternative energy source since it does not come from fossil fuels, offering a sustainable solution for meeting energy needs while mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, there are three main types of biomass: residual (such as agricultural and forestry residues), natural (like wood), and generated (like sewage and urban organic waste).
How is biomass energy generated?
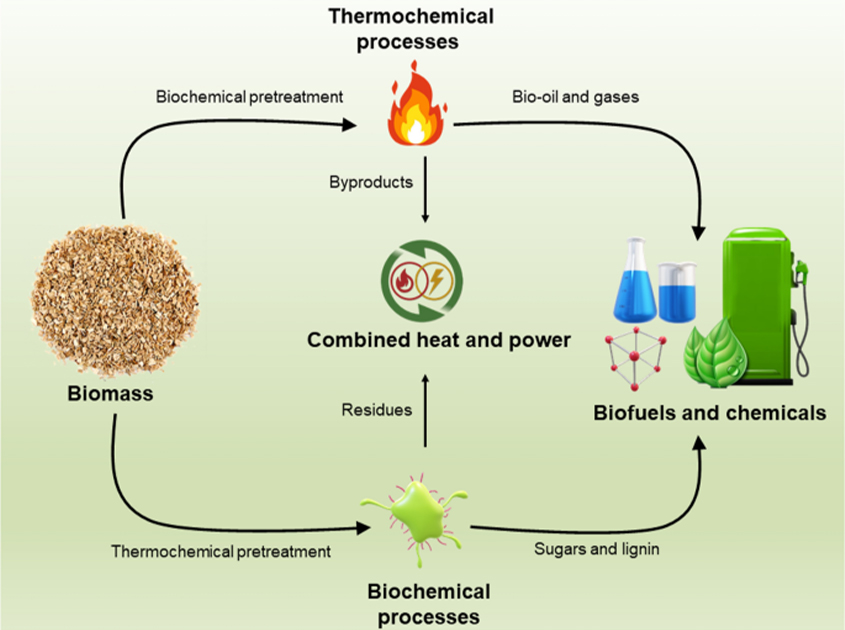
Various processes can transform biomass into usable energy forms, including:
- Direct combustion: Direct combustion stands as the predominant approach in harnessing energy from biomass. It involves burning biomass directly to heat buildings and water, to supply industrial process heat, and to produce electricity through steam turbines.
- Thermochemical conversion: High-temperature treatment without oxygen produces synthesis gas or bio-oils. These can become biofuels or chemicals.
- Chemical conversion: Employing chemical treatments and processes like transesterification to convert plant-based oils and fats into biodiesel.
- Biological conversion: Using enzymes and microorganisms to break down biomass into gaseous or liquid biofuels like biogas (from anaerobic digestion of animal waste or sewage sludge) and ethanol (from fermentation of plant-derived sugars).
These diverse conversion methods enable the utilisation of a wide range of biomass feedstocks, making biomass a versatile and renewable source of energy that can supplement or replace conventional fossil fuels in various applications. Moreover, scientists and researchers are actively exploring ways to enhance existing biomass conversion methodologies and develop novel techniques to harness a greater portion of available biomass resources for energy production.
Advantages of Biomass energy
Biomass energy boasts various benefits compared to fossil fuels, with its most prominent advantage being its role in mitigating carbon emissions in the atmosphere. This mitigation is achieved through a closed carbon cycle, where the carbon dioxide released during biomass combustion is recaptured by growing plants, unlike fossil fuels which release long-sequestered carbon. The thermal processing of biomass for energy generation further reduces net carbon emissions compared to fossil fuel processing. Due to its renewable nature and the potential for carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative outcomes when combined with advanced technologies like carbon capture and storage.
Consequently, the utilisation of biomass presents numerous advantages that render it an appealing choice for energy generation and reducing the carbon footprint across various sectors:
- Companies utilize urban and industrial waste biomass, typically sourced locally, thereby closing the loop without requiring transportation and fostering the circular economy.
- Biomass derived from pruning and forest maintenance waste is utilised, thereby mitigating the risk of forest fires.
- It creates long-term, local job prospects in the green energy sector, reducing carbon emissions associated with long-distance commuting and fostering sustainable community development.
- In contrast to fossil fuels, biofuels derived from biomass offer a lower-carbon alternative for transportation, particularly in hard-to-decarbonize sectors like aviation.
- It lessens reliance on fossil fuels in industrial processes, providing a renewable alternative that can significantly reduce carbon emissions in manufacturing and production.
- In regions heavily dependent on imported fossil fuels, biomass serves as a vital asset in reducing the carbon footprint associated with fuel transportation and geopolitical energy dependencies.
- The utilisation of biomass encourages efficient land use and conservation practices, promoting carbon sequestration through responsible agricultural and forestry management.
- By using agricultural residues for energy production, the carbon footprint of farming is reduced, while also providing farmers with an additional income stream from waste products.
- It serves as a vital asset in tackling energy poverty in areas where spending on fossil fuels constitutes a substantial portion of their Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Modern biomass technologies offer higher energy efficiency than some fossil fuel processes. This further reduces energy production’s carbon footprint.
- The use of biomass can be integrated with carbon capture and storage technologies, potentially creating negative emissions scenarios that actively remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.

Is biomass energy renewable or nonrenewable?
Biomass is regarded as a renewable energy source due to the fact that its inherent energy originates from the sun, and it possesses the ability to regenerate within a relatively short period. This characteristic implies that biomass can be utilised continuously without risking depletion or exhaustion of the resource. Additionally, it can be replenished at a relatively rapid pace, thereby avoiding the irreversible diminishment of the Earth’s natural reserves.
The formation of fossil fuels requires several thousand or even millions of years. However, the growth cycle of a tree spans only 30 years, corn stalks are produced annually, and animal manure is generated daily. Given the abundance and ease of replenishment of biomass materials, they are classified as renewable energy sources.
Current applications and potential of Biomass
According to data, biomass contributed approximately 4.7% of the total primary energy consumption in the United States during the year 2020. The utilisation of biomass was distributed across various sectors, with the following breakdown:
- 50% Industrial
- 28% Transportation
- 10% Residential
- 9% Electric power
- 3% Commercial
The United Kingdom is home to numerous biomass power facilities that play a crucial role in diversifying the country’s renewable energy portfolio. As of 2023, there were 78 operational power plants in the UK that utilised biomass resources to produce electricity. Collectively, these installations had an estimated power generation capacity of 4,158 megawatts, sufficient to meet the hourly electricity needs of approximately 8.3 million residential households.
Another instance of biomass utilisation originates from the Beijing Dequingyuan chicken farm, where three million chickens yield 220 tons of manure daily. Employing gasification technology, the farm transforms this manure into 14,600 megawatt-hours of electricity annually.
How safe is biomass energy?
Biomass energy is regarded as a secure energy source. Nevertheless, it doesn’t imply that biomass energy doesn’t possess certain drawbacks, particularly when considering its environmental cleanliness.
Pollutants pose a significant potential concern. The combustion of biomass emits pollutants and particulate matter into the atmosphere, including greenhouse gases that are notorious for their contribution to global warming. However, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) within the United States has implemented regulations aimed at mitigating the potential adverse effects of biomass energy generation on the environment.
Other drawbacks of biomass do not necessarily compromise the safety of biomass energy. While there are several additional aspects to consider, the advantages of biomass far surpass both its drawbacks and those of continued fossil fuel combustion.

Is Energy from Biomass Efficient?
Biomass presents a renewable energy alternative that can readily substitute for conventionally utilised fossil fuels, simultaneously providing numerous beneficial environmental impacts. The efficiency of converting biomass into usable forms such as electricity, thermal energy, transportation fuels, and chemical products heavily relies on the specific conversion processes employed.
Nevertheless, similar to any other energy source, efficiency can be further optimised by utilising appropriate technological tools. By implementing the right energy management software, you can monitor, analyse, and control the usage of biofuel along with other energy sources such as electricity, gas and thermal. If the software identifies excessive biomass consumption, you possess the capability to modify the consumption rate or upgrade to a more efficient boiler system, thereby optimising biomass usage.
So how can we enhance the effectiveness of contemporary installations?
Vinergy‘s intelligent solution empowers you to optimise your installation’s efficiency with its data-driven insights, allowing you to make the necessary adjustments for peak performance.
